Lung Cancer Diagnosis Clinical Decision Support System
The purpose of this system is to help doctors diagnose of lung cancer. It supports diagnosis by deep learning based on 3d detection and classification nodules.
My Role
Project Leader
- Design a whole data pipeline
- Implement DICOM-based data preprocessing module
- Design and implement 3D U-net based detection neural network
- Design and implement 3D Resnet based classification neural network
Project Detail
Lung cancer is ranks highly among all causes in death rate. In 2015, 17,399 people were killed by lung cancer in Korea, making up 27.9% of all cancer related deaths. The reason for its high death rate is the lack of an efficient inspection process.
In many cases, a biopsy is taken to confirm whether a patient has lung cancer or not. It, however, should be avoided as much as possible since it is an invasive inspection. Typically a chest computed tomography (CT) is used for biopsy screening, so a radiologist’s ability to read the CT correctly is very important.
To better share experience accumulated over time, decision support system based on AI have been widely adopted in various industrial fields. In the medical domain, the need for a quick and precise diagnosis decision is intensifying. Hence, this kind of system has been researched by many scientists and Medipixel’s lung cancer project is designed to fulfill those needs. We worked jointly with Asan Medical Center and ended up developing the Lung Cancer Diagnosis Clinical Decision Support System.
It has the following advantages
- Detects nodules that can be missed → increased diagnosis accuracy
- Assists doctors to read chest CT scan with ease → increased diagnosis productivity
![]()
System Features
The system features are below
- Supports diagnosis process of whether nodule is malignant or benign
- Handles non-small cell lung cancer nodule in the 10mm~30mm range
- Shows the number of nodules and nodule region of interests
- Indicates estimated lung cancer risk percentage
![]()
Tasks
I was involved as a project leader who was in charge of designing the overall process and data flow.
I decided to approach this project with a practical view. Since most processes in deep learning system are formulaic, I did not focus on designing a system structure. Making a completely new model was not a focus either. Instead, we put more time into finding a high performance model adopted in the medical domain and improving upon it.
Dataset
One of the most important issues in a deep learning system is how to gather and handle a proper dataset. We utilized several dataset, of hospitals involved with Asan Medical Center and an open dataset like NLST to improve performance of the system. There were some issues with these datasets as follows
- Different data format (especially open data-set)
- Different data modality such as resolution of CT
- Overwhelmingly numerous malignant nodules (more than benign nodules)
- Difficulty with finding completely negative data which did not have any nodule
Preprocess
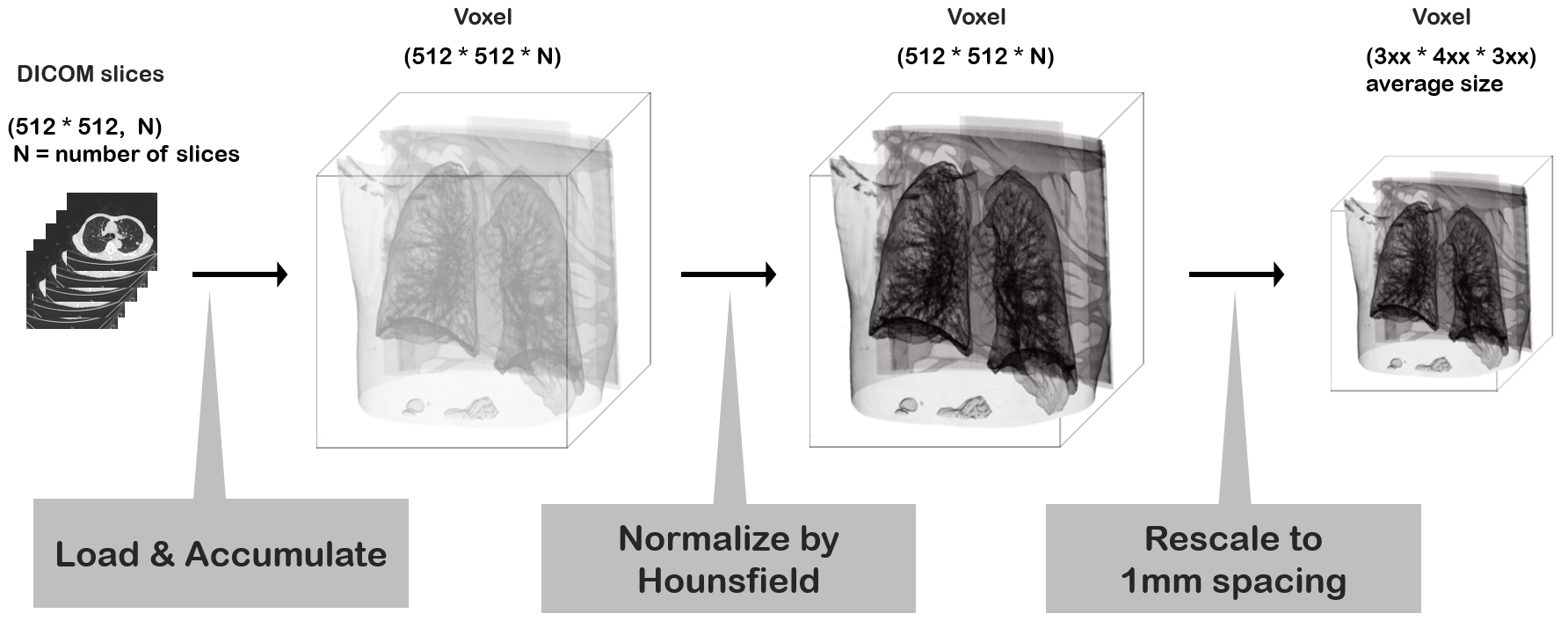
We had to preprocess a heterogeneous dataset through one pipeline. Basically, it was necessary to reconstruct and normalize from 2d DICOM slices to 3d voxel data. Since this task was expected to take a long time, it had to be done in advance, and the results saved to a hard disk before we could with the proceed regular training process. Main process was as follows.
- Perform 3D reconstruction with a thickness of 1mm
- Set Hounsfield Unit between -1200 and 600
- Normalize each pixel value between 0 and 255
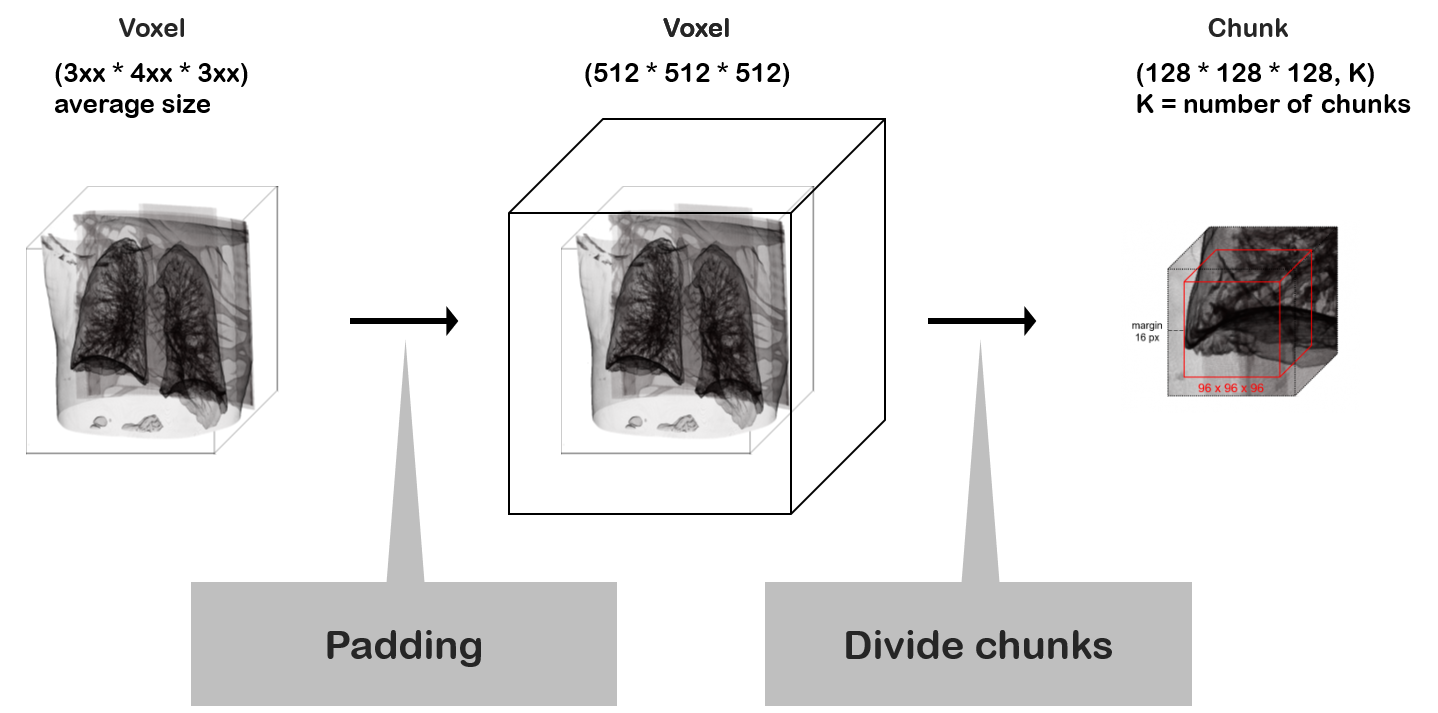
Rather than using the whole voxel data, it was divided into smaller chunks due to GPU memory limitation. This process occurred in the training and inference routines.
Gathering Dataset
To improve performance, we needed to obtain more datasets from various sources. The process of collecting proper data for modeling requires a significant time cost for doctors. Data labeling, especially, requires significant time because it is an arduous task to segment the region of nodule pixel by pixel.
We exerted much effort to help them. To improve efficiency and decrease the time required, we had several meetings with doctors and proposed useful methods such as a nodule segmentation support application and semi-auto segmentation for nodule data.

Deep Learning Networks
During the research period, I realized that an ensemble strategy was efficient to improve whole system accuracy. After many experiments using various models, I tried to find the optimal combination. As a result we decided to use three Deep Neural Network(DNN) networks in the system.
Detection Network
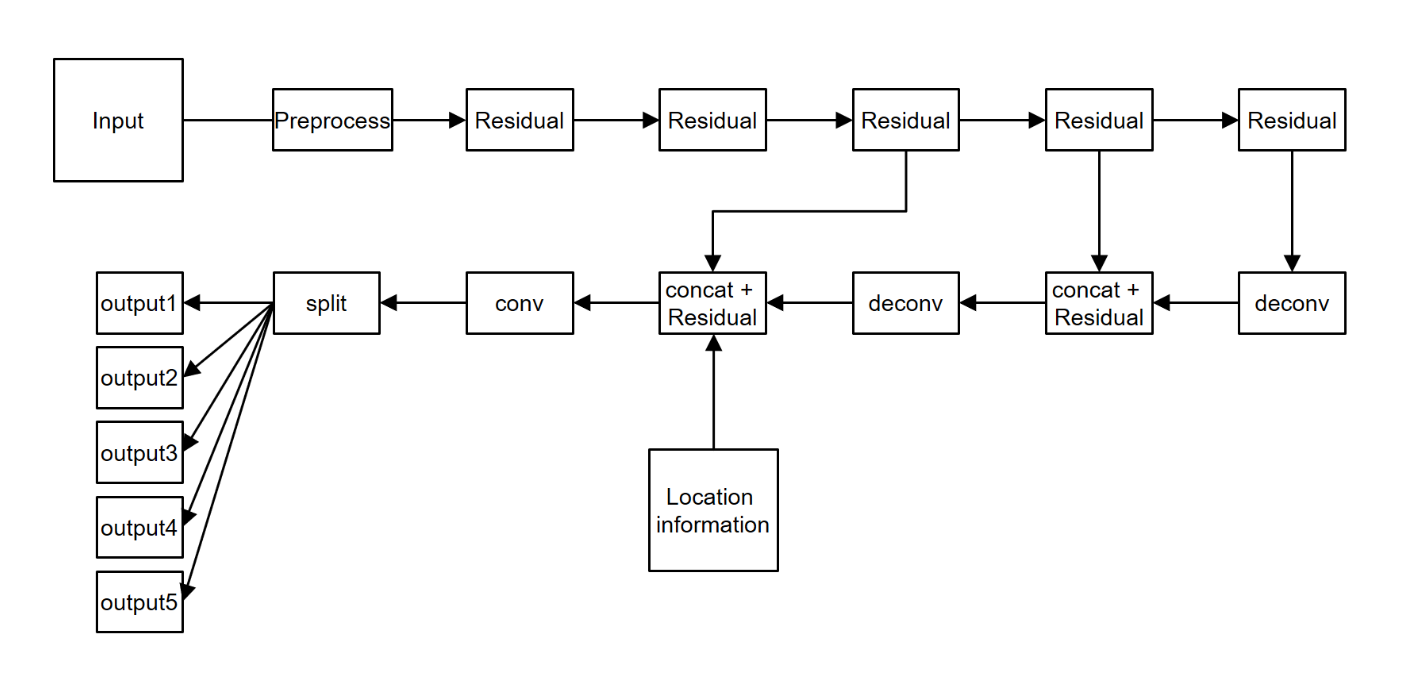
This network detects nodules. It is built based on 3d U-net. Detection network consists of an encoding and decoding network. The nodule’s features are extracted in the encoding network through 3D residual blocks.
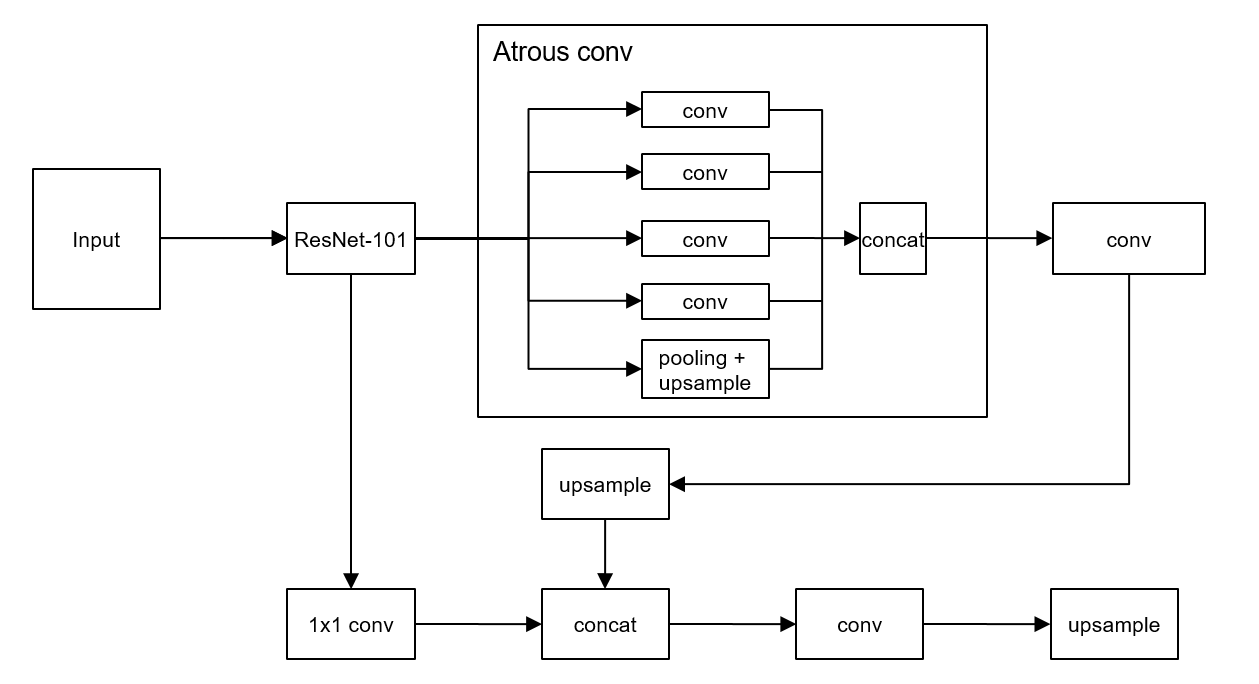
Segmentation Network
This network performs segmentation of nodules in each slide based on the results from the detection network. Its second role is to act as a filter for false-positive regions. Our segmentation network takes advantage of the Deeplab-v3+ network whose network structure is shown in figure below
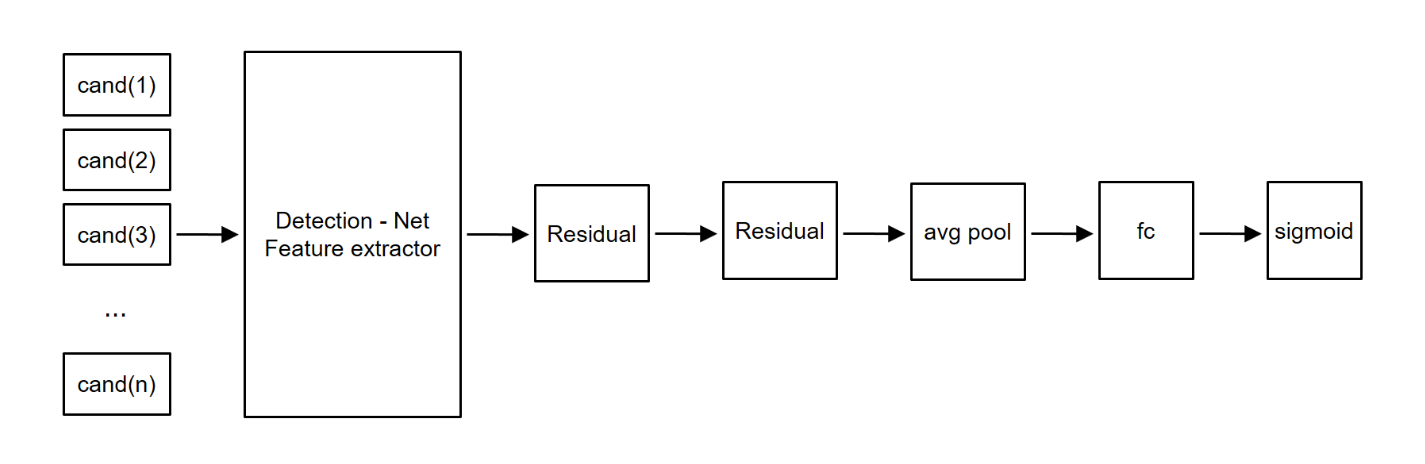
Classification Network
The classification network is responsible for determining the degree of malignancy of candidate nodules. Features of nodules are extracted through the 3D residual network layer, and we made final result from the extracted features.
Practical Technique
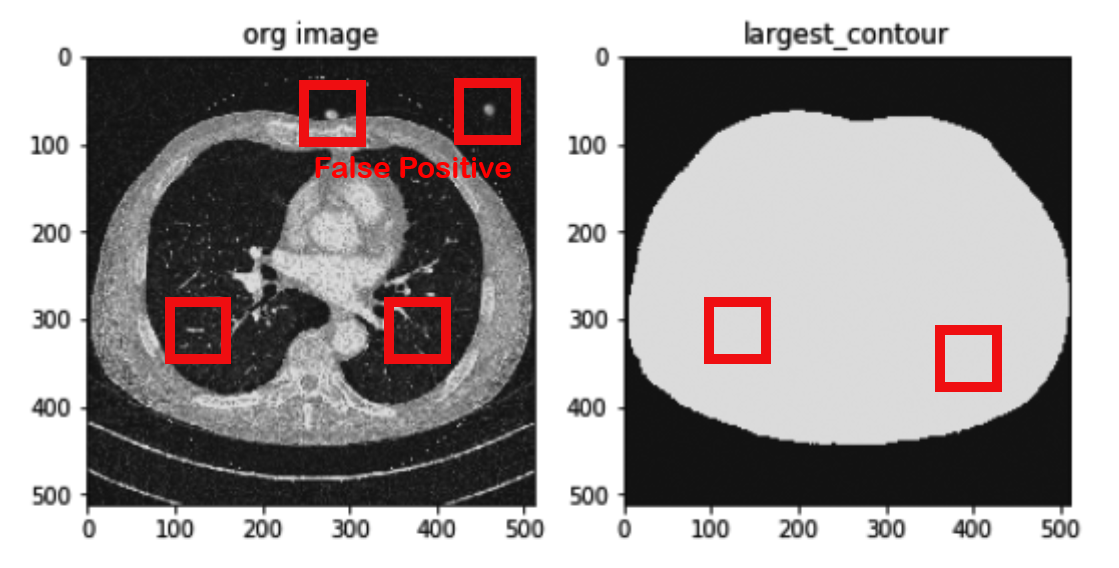
I also added a simple preprocess stage before the segmentation network to get rid of nodules in the outer body. This stage was composed of a simple method that checks the largest contour and erodes it. It mapped a candidate nodule region onto 2D slide and examined whether it belongs to the inside of the body. Then any regions outside of the body were removed as false-positives. This method has some advantages over other methods that perform complicated lung-segmentation as follows
- It is much faster than a conventional segmentation method via complex algorithm
- It removes an ordinary lung-segmentation algorithm problem that recognizes a nodule on the wall as outside the lung
- It solves a region segmentation error resulting from different modality such as different CT slide scanner
Strengths of the Structure
Generally, most cancer diagnosis systems have a similar structure. Among these systems, combinations with U-net based detector and classifier are popular. I embedded simple preprocess stage and segmentation network in center of this combination. The network mapped 3d suspicious chunks to 2d CT slice, and, at the same time, performed to segment area in suspicious chunks. In this context, segmentation means scrutinizing and filtering nodules. So, I was able to remove many false positive nodules from the results in the first stage. From those features, the system gained a simple but powerful improvement.
![]()
Conclusion
Through interviews, we found that time spent on reading chest CT generally takes about from five to twenty minutes. Our system achieved satisfying results that reduce time to under one minute while maintaining over 90% accuracy.
TSNE result was like below
![]()
Patent
[1] Pathological diagnosis method and apparatus based on machine learning 10-2020-0082660